This Microsoft Power Automate post will show how to create a list with Power Automate Desktop.
Microsoft Power Automate Desktop is an invaluable tool for data management and workflow automation.
Create a List
The process begins by setting up a new list through the “Create new list” action. This is the initial step to organizing your data for automated processes.
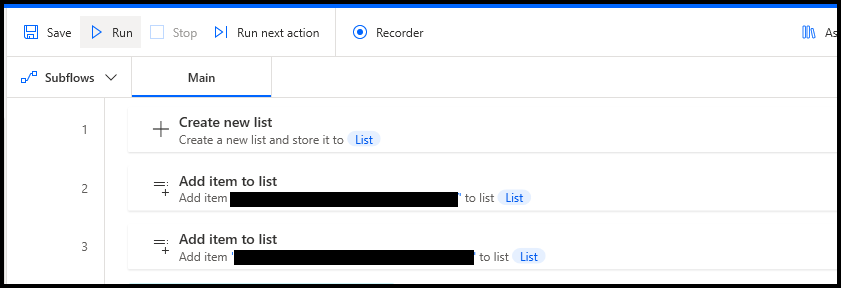
After creating the list, the next step involves populating it with desired items. This is achieved using the “Add item to list” action. You can repeatedly add various items to tailor the list according to the needs of your specific workflow or project requirements.
The true potential of using lists in automation is unlocked through the application of loops. As illustrated in the second image, you can use a loop to iterate over each item in the list. This capability allows for the execution of repetitive tasks automatically and efficiently within your workflow.
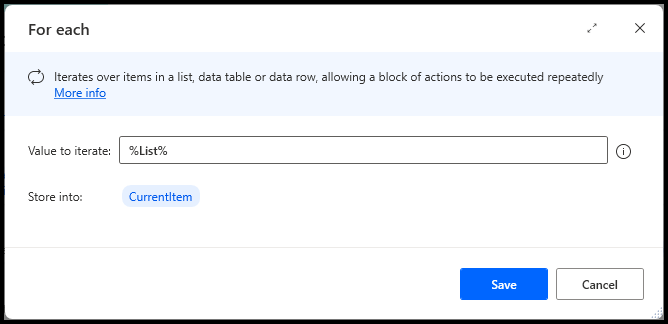
Within the loop, you can insert various actions and tasks that apply to each item. These tasks might include processing data, performing calculations, or interacting with other software tools.
This method not only saves significant time over manual operations but also enhances accuracy and ensures consistency across tasks.
Implementing loops and lists in Power Automate Desktop facilitates complex data operations and automates routine tasks. Whether you are managing large datasets or performing frequent updates, these tools provide robust solutions that integrate seamlessly with other Microsoft applications.
This tutorial demonstrates just the beginning of what’s possible with Power Automate Desktop. By mastering these foundational elements, you can expand your automation capabilities, making your processes more efficient and your workload more manageable. Learn these steps to transform the way you handle workflow automation with Power Automate Desktop.
Related Articles
- How to Create Multiple Storage Accounts on Azure Using Bicep Loops
- Add Loops, Conditions and Functions to ASP.NET Core Razor Pages
- Configuring Power Plan Using Group Policy For Windows 7
- Find the Default Power Platform Environment Using PowerShell
- Export a List of All Power Platform Environments to CSV Using